- Print
- DarkLight
- PDF
Deploy Azure Functions for PowerShell on Linux OS
- Print
- DarkLight
- PDF
This article aims to help you deploy Azure Functions for PowerShell on Linux OS in your environment using Infrastructure-as-Code with Azure Bicep.
Azure Bicep is a domain-specific language (DSL) that uses a declarative syntax to deploy Azure resources.
The Bicep is an abstraction on top of Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates to define Azure resources using declarative Infrastructure as Code.
During Microsoft Ignite 2022, it was announced the Azure Functions support for PowerShell on Linux OS is generally available in Azure Functions runtime 4.0 on all hosting plans.
You can now develop Azure Functions PowerShell apps locally and deploy them to Azure Functions on Linux OS.
This article will show how you can deploy Azure Functions for PowerShell on Linux OS using Azure Bicep, a Domain Specific Language (DSL), for deploying Azure resources declaratively.
Prerequisites
• An Active Azure account: You can create an account for free.
• Azure Bicep is installed on your local machine.
• Azure PowerShell. See: Install Azure PowerShell.
• A resource group in your Azure subscription
Let's get started!
1. Solution Overview
We will author a Bicep template that creates an Azure Function for PowerShell on Linux OS.
The solution will include the following files:
• 📄 main.bicep: This is the Bicep template
• 📄 azuredeploy.parameters.json: This parameter file contains the values to use for deploying your Bicep template.
2. Azure Bicep Template — parameters
Create a new file in your working directory and name it main. Bicep. We will define the following parameters:
param functionAppName string
param location string
param hostingPlanName string
param alwaysOn bool
param use32BitWorkerProcess bool
param ftpsState string
param storageAccountName string
param linuxFxVersion string
param sku string
param skuCode string
@description('Storage Account type')
@allowed([
'Standard_LRS'
'Standard_GRS'
'Standard_RAGRS'
])
param storageAccountType string = 'Standard_LRS'
3. Azure Bicep Template — variables
We will define the following variable:
var applicationInsightsName = functionAppName
4. Azure Bicep Template — resources
We will define the following resources:
resource storageAccount 'Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts@2021-02-01' = {
name: storageAccountName
location: location
sku: {
name: storageAccountType
}
kind: 'Storage'
}
resource hostingPlan 'Microsoft.Web/serverfarms@2021-02-01' = {
name: hostingPlanName
location: location
kind: 'linux'
properties: {
reserved: true
zoneRedundant: true
}
sku: {
tier: sku
name: skuCode
}
}
resource applicationInsights 'microsoft.insights/components@2020-02-02' = {
name: applicationInsightsName
location: location
tags: {
'hidden-link:${resourceId('Microsoft.Web/sites', applicationInsightsName)}': 'Resource'
}
properties: {
Application_Type: 'web'
}
kind: 'web'
}
resource functionApp 'Microsoft.Web/sites@2022-03-01' = {
name: functionAppName
kind: 'functionapp,linux'
location: location
properties: {
siteConfig: {
appSettings: [
{
name: 'FUNCTIONS_EXTENSION_VERSION'
value: '~4'
}
{
name: 'FUNCTIONS_WORKER_RUNTIME'
value: 'powershell'
}
{
name: 'APPINSIGHTS_INSTRUMENTATIONKEY'
value: reference('microsoft.insights/components/azinsiderfun', '2015-05-01').InstrumentationKey
}
{
name: 'APPLICATIONINSIGHTS_CONNECTION_STRING'
value: reference('microsoft.insights/components/azinsiderfun', '2015-05-01').ConnectionString
}
{
name: 'AzureWebJobsStorage'
value: 'DefaultEndpointsProtocol=https;AccountName=${storageAccountName};AccountKey=${listKeys(storageAccount.id, '2019-06-01').keys[0].value};EndpointSuffix=core.windows.net'
}
]
cors: {
allowedOrigins: [
'https://portal.azure.com'
]
}
use32BitWorkerProcess: use32BitWorkerProcess
ftpsState: ftpsState
linuxFxVersion: linuxFxVersion
alwaysOn: alwaysOn
}
serverFarmId: hostingPlan.id
clientAffinityEnabled: false
virtualNetworkSubnetId: null
httpsOnly: true
}
dependsOn: [
applicationInsights
]
}
5. Parameters file
Create a new file named azuredeploy.parameters.json. The code below shows the definition of the parameters file:
{
"$schema": "https://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2015-01-01/deploymentParameters.json#",
"contentVersion": "1.0.0.0",
"parameters": {
"functionAppName": {
"value": "azinsiderfun"
},
"location": {
"value": "East US"
},
"hostingPlanName": {
"value": "ASP-azinsiderdemo-ba3e"
},
"alwaysOn": {
"value": true
},
"ftpsState": {
"value": "FtpsOnly"
},
"storageAccountName": {
"value": "azinsiderdemob924"
},
"sku": {
"value": "PremiumV2"
},
"skuCode": {
"value": "P1v2"
},
"use32BitWorkerProcess": {
"value": false
},
"linuxFxVersion": {
"value": "PowerShell|7.2"
}
}
}
6. Azure Bicep Template — Deployment
We will use the command below to deploy our Bicep template:
$date = Get-Date -Format "MM-dd-yyyy"
$rand = Get-Random -Maximum 1000
$deploymentName = "AzInsiderDeployment-"+"$date"+"-"+"$rand"
New-AzResourceGroupDeployment -Name $deploymentName -ResourceGroupName azinsider_demo -TemplateFile .\main.bicep -TemplateParameterFile .\azuredeploy.parameters.json -c
The image below shows the preview of the deployment:
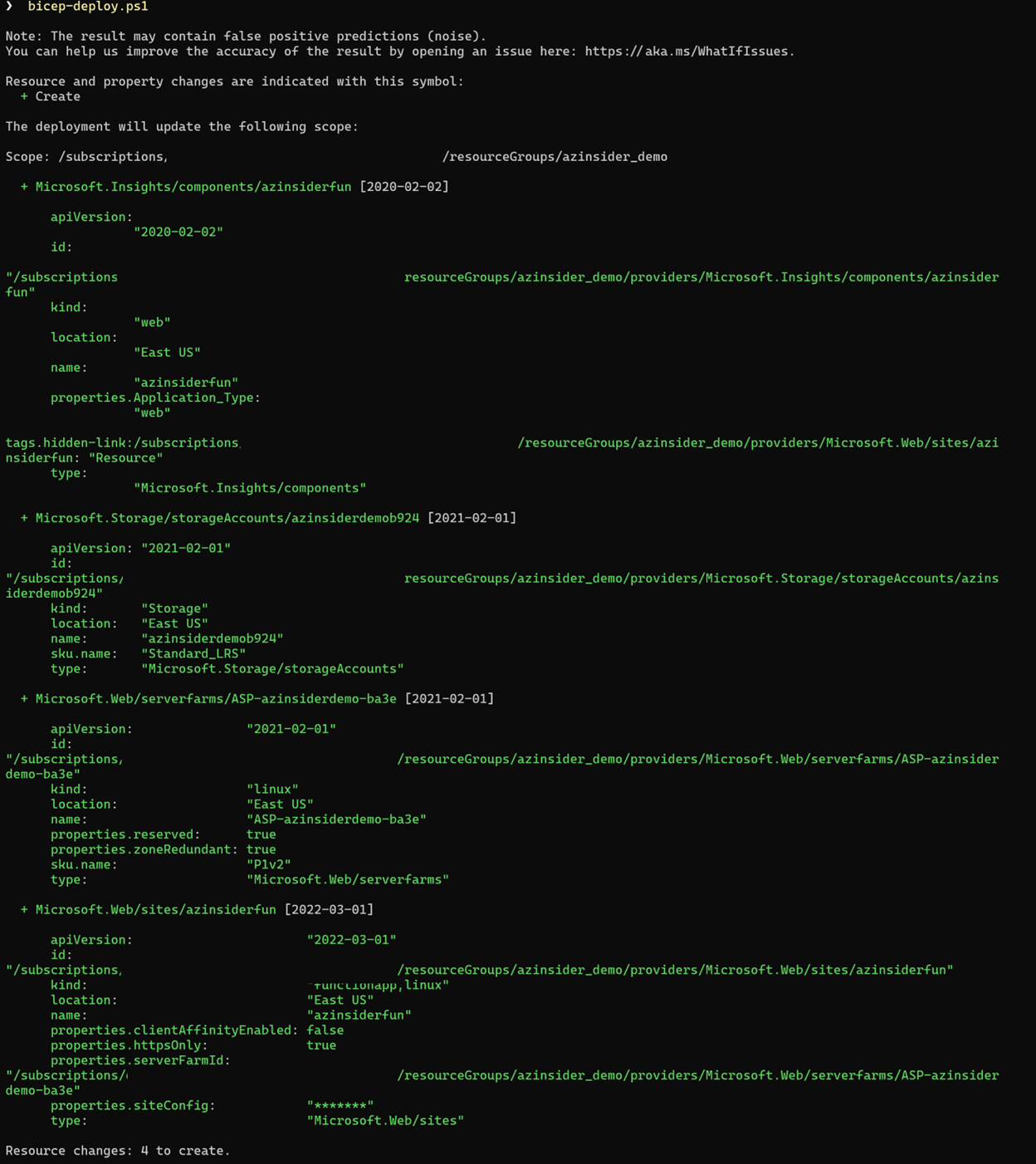
Then we will execute the deployment. The image below shows the deployment output:
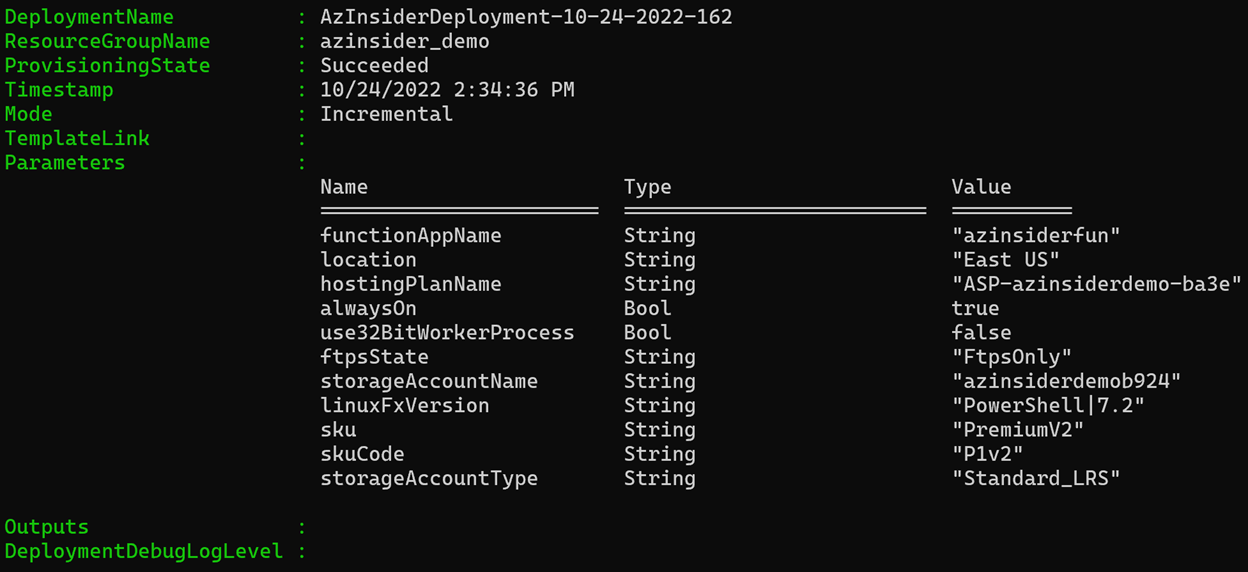
You can find the code of this solution in the following URL; feel free to contribute!
https://github.com/daveRendon/azinsider/tree/main/application-workloads/azure-functions-for-powershell-linux
You can go to the Azure Portal and review the configuration of the Azure Function resource type as shown below:
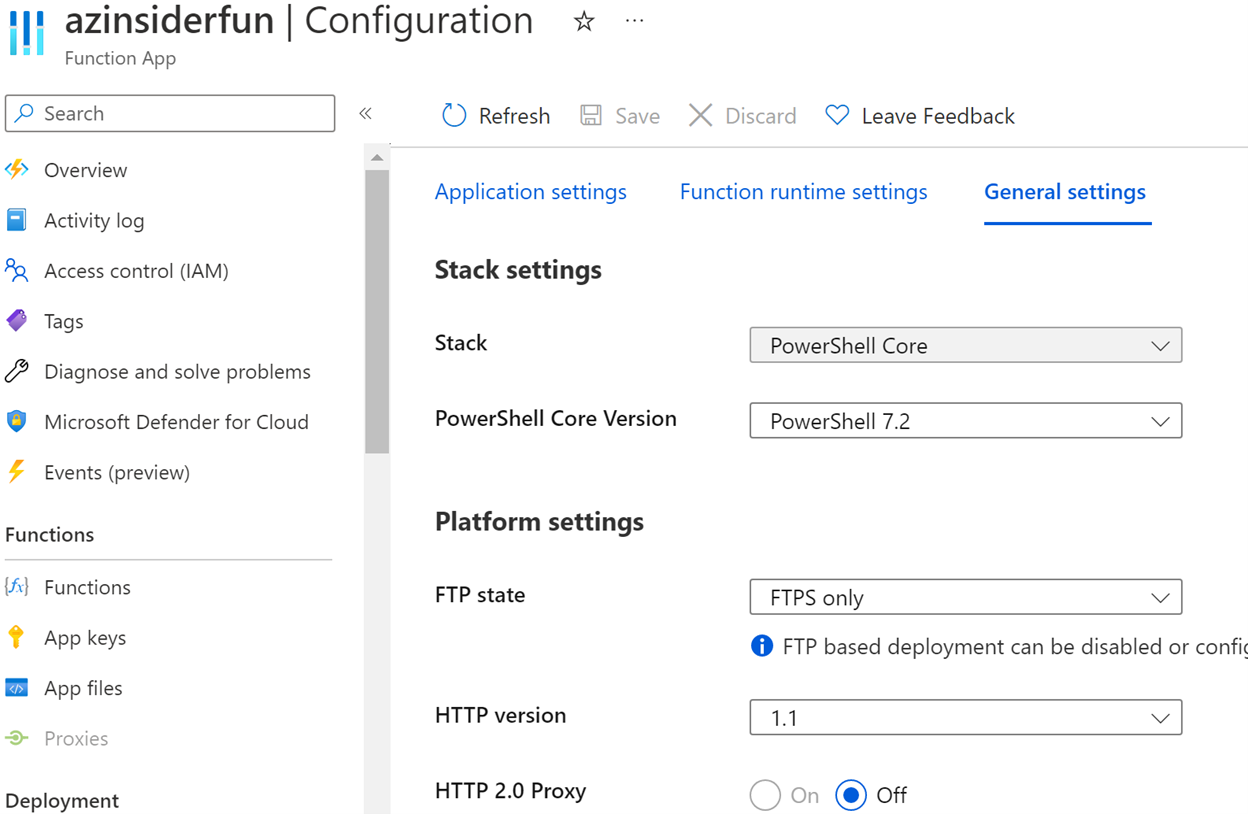
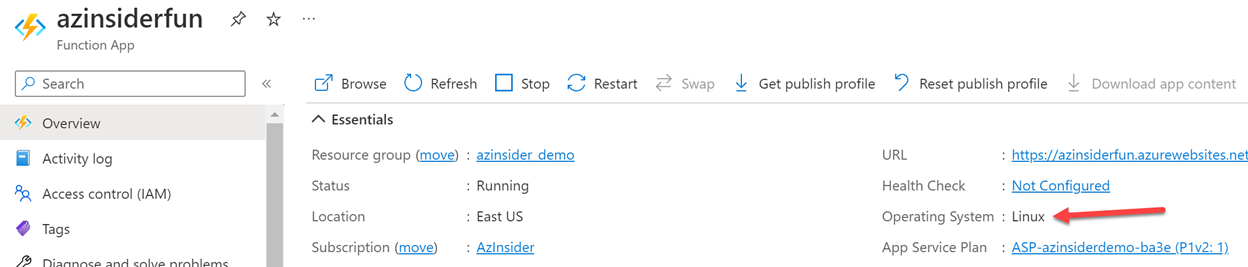
Note that the configuration reflects the use of PowerShell Core 7.2. We can also validate the OS in the overview tab, as shown below:
Conclusion
This article reviewed how to leverage Infrastructure-as-Code using Azure Bicep to deploy Azure Functions for PowerShell on Linux OS.

