- Print
- DarkLight
- PDF
Create Event Hubs Namespace and VNet integration
- Print
- DarkLight
- PDF
This article aims to help you deploy a new Event Hub Namespace and Vnet integration in your environment using Infrastructure-as-Code with Azure Bicep.
Azure Bicep is a domain-specific language (DSL) that uses a declarative syntax to deploy Azure resources.
The Bicep is an abstraction on Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates to define Azure resources using declarative Infrastructure as Code.
Prerequisites
• An Active Azure account: You can create an account for free.
• Azure Bicep is installed on your local machine.
• Azure PowerShell. See: Install Azure PowerShell.
• A resource group in your Azure subscription
Let's get started!
1. Solution Overview
We will author a Bicep template that creates an Event Hub Namespace and the configuration for the VNet integration.
The solution will include the following files:
• 📄 main.bicep: This is the Bicep template with the actual resources
• 📄 azuredeploy.parameters.json: This parameter file contains the values for deploying your Bicep template.
2. Azure Bicep Template — parameters
Please create a new file in your working directory and name it main. Bicep. We will define the following parameters:
@description('Name of the Event Hubs namespace')
param eventhubNamespaceName string
@description('Name of the Virtual Network')
param vnetName string
@description('Name of the Virtual Network Sub Net')
param subnetName string
@description('Location for Namespace')
param location string = resourceGroup().location
3. Azure Bicep Template — variables
We will define the following variables:
var namespaceVirtualNetworkRuleName = '${eventhubNamespaceName}/${vnetName}'
var subNetId = resourceId('Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks/subnets/', vnetName, subnetName)
4. Azure Bicep Template — resources
We will define the following resources:
resource eventhubNamespace 'Microsoft.EventHub/namespaces@2018-01-01-preview' = {
name: eventhubNamespaceName
location: location
sku: {
name: 'Standard'
tier: 'Standard'
}
properties: {
}
}
resource vnetRule 'Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks@2017-09-01' = {
name: vnetName
location: location
properties: {
addressSpace: {
addressPrefixes: [
'10.0.0.0/23'
]
}
subnets: [
{
name: subnetName
properties: {
addressPrefix: '10.0.0.0/23'
serviceEndpoints: [
{
service: 'Microsoft.EventHub'
}
]
}
}
]
}
}
resource eventhubNamespaceVnetRule 'Microsoft.EventHub/namespaces/VirtualNetworkRules@2018-01-01-preview' = {
name: namespaceVirtualNetworkRuleName
properties: {
virtualNetworkSubnetId: subNetId
}
dependsOn: [
eventhubNamespace
]
}
5. Parameters file
Create a new file named azuredeploy.parameters.json. The code below shows the definition of the parameters file:
{
"$schema": "https://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2019-04-01/deploymentParameters.json#",
"contentVersion": "1.0.0.0",
"parameters": {
"eventhubNamespaceName": {
"value": "azinsidreventhub" // Your event hub namespace name
},
"vnetName": {
"value": "azinsidr-vnet" // Your vnet name
},
"subnetName": {
"value": "default" // Your subnet name
}
}
}
6. Azure Bicep Template — Deployment
We will use the command below to deploy our Bicep template:
$date = Get-Date -Format "MM-dd-yyyy"
$rand = Get-Random -Maximum 1000
$deploymentName = "AzInsiderDeployment-"+"$date"+"-"+"$rand"
New-AzResourceGroupDeployment -Name $deploymentName -ResourceGroupName azinsider_demo -TemplateFile .\main.bicep -TemplateParameterFile .\azuredeploy.parameters.json -c
The image below shows the preview of the deployment:
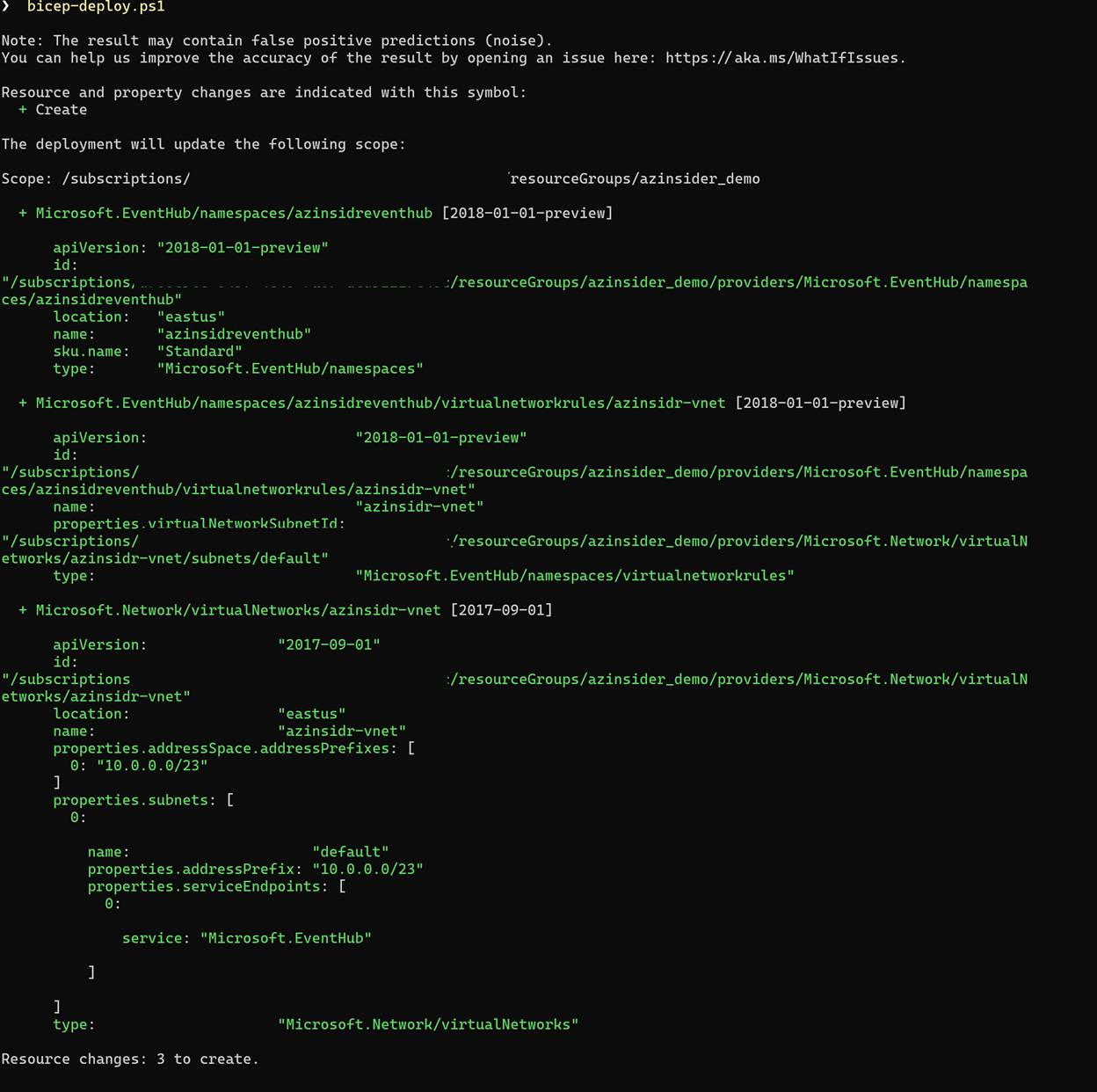
Then we will execute the deployment. The image below shows the deployment output:
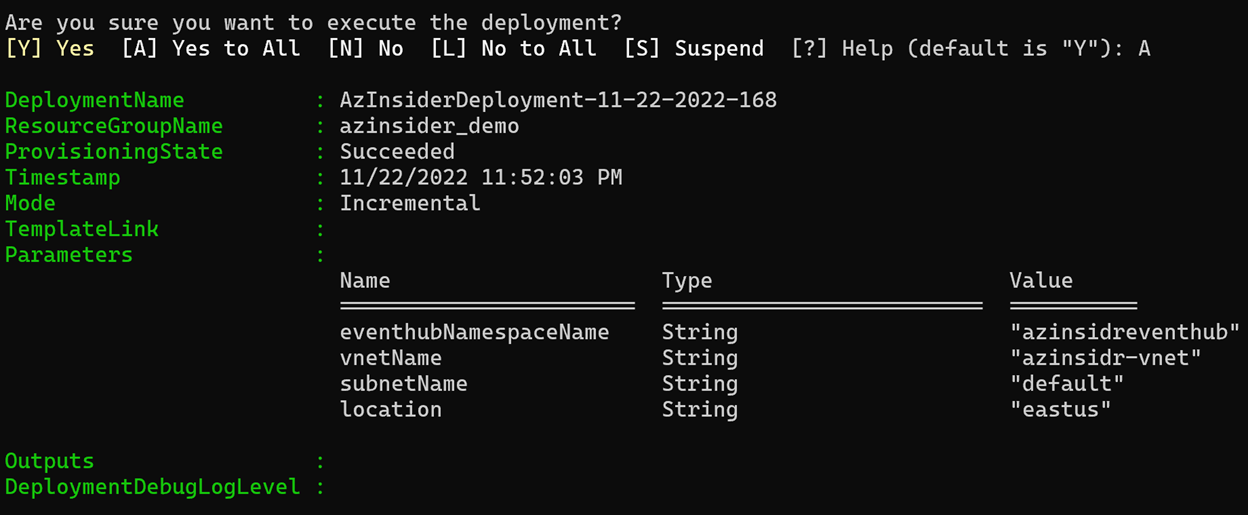
You can verify the resources deployed using the Azure Portal as shown below:
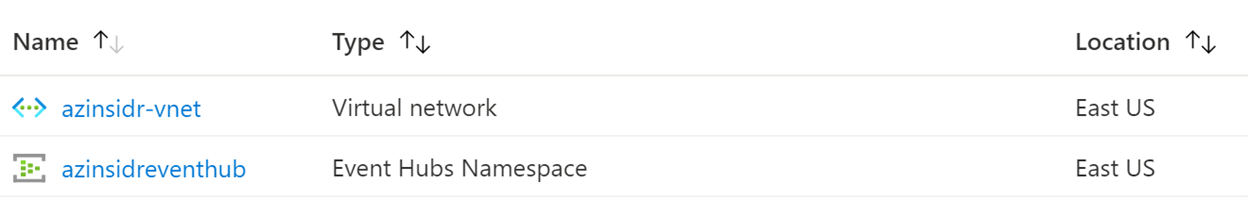
Finally, validate the configuration in the virtual network:
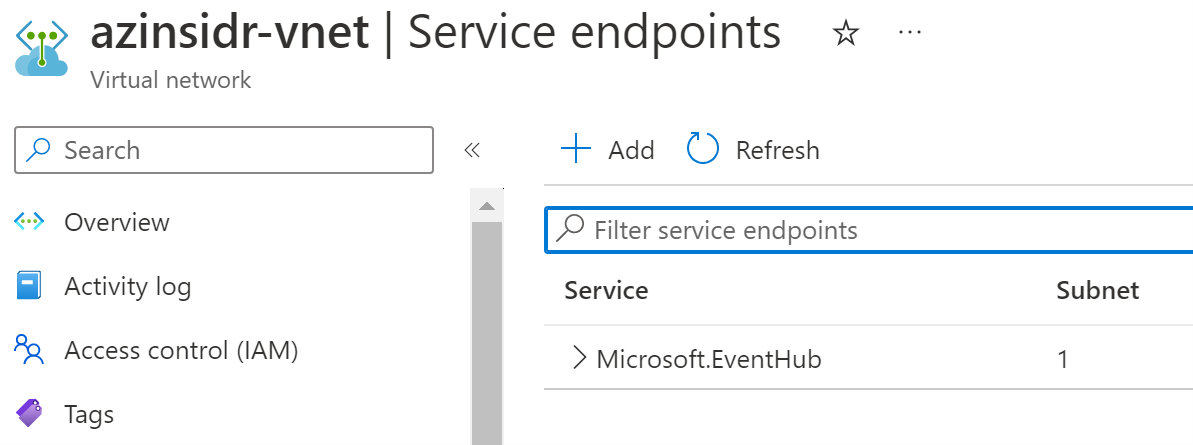
Source Code
You can find the code of this solution in the following URL. Feel free to contribute!

