- Print
- DarkLight
- PDF
Deploy Azure Container Apps using Bicep
- Print
- DarkLight
- PDF
The purpose of this article is to help you deploy Azure Container Apps in environment using Infrastructure-as-Code with Azure Bicep. Azure Container Apps enables you to run microservices and containerized applications on a serverless platform.
Azure Bicep is a domain-specific language (DSL) that uses a declarative syntax to deploy Azure resources.
Bicep is an abstraction on top of Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates to define Azure resources using declarative Infrastructure as Code.
Why Azure Container Apps?
Azure Container Apps comprises a set of multiple capabilities including:
• Deploying API endpoints
• Hosting background processing applications
• Handling event-driven processing
• Running microservices
Applications built on Azure Container Apps can dynamically scale based on the following characteristics:
• HTTP traffic
• Event-driven processing
• CPU or memory load
• Any KEDA-supported scaler
This article will show how you can deploy Azure Container Apps using Azure Bicep, a Domain Specific Language (DSL) for deploying Azure resources declaratively.
Prerequisites
• An Active Azure account: You can create an account for free.
• Azure Bicep is installed on your local machine.
• Azure PowerShell. See: Install Azure PowerShell.
• A resource group in your Azure subscription
Let’s get started!
Solution Overview
We will author a Bicep template that deploy Azure Container Apps. The solution will include the following files:
• 📄 main.bicep: This is the Bicep template that will deploy the actual resources
• 📄 azuredeploy.parameters.json: This parameter file contains the values to use for deploying your Bicep template.
## 2. Azure Bicep Template — parameters
Create a new file in your working directory and name it main.bicep . We will define the following parameters:
param name string
param location string
param environmentId string
param containers array
@secure()
param secrets object
param registries array
param ingress object
param environmentName string
param workspaceName string
param workspaceLocation string
3. Azure Bicep Template — resources
We will define the following resources:
resource name_resource 'Microsoft.App/containerApps@2022-06-01-preview' = {
name: name
location: location
properties: {
environmentId: environmentId
configuration: {
secrets: secrets.arrayValue
registries: registries
activeRevisionsMode: 'Single'
ingress: ingress
}
template: {
containers: containers
scale: {
minReplicas: 0
}
}
}
dependsOn: [
environment
]
}
resource environment 'Microsoft.App/managedEnvironments@2022-06-01-preview' = {
name: environmentName
location: location
properties: {
appLogsConfiguration: {
destination: 'log-analytics'
logAnalyticsConfiguration: {
customerId: reference('Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/${workspaceName}', '2020-08-01').customerId
sharedKey: listKeys('Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/${workspaceName}', '2020-08-01').primarySharedKey
}
}
}
sku: {
name: 'Consumption'
}
dependsOn: [
workspace
]
}
resource workspace 'Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces@2020-08-01' = {
name: workspaceName
location: workspaceLocation
properties: {
sku: {
name: 'PerGB2018'
}
retentionInDays: 30
workspaceCapping: {
}
}
dependsOn: []
}
4. Parameters file
Create a new file named azuredeploy.parameters.json. The code below shows the definition of the parameters file:
{
"$schema": "https://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2015-01-01/deploymentParameters.json#",
"contentVersion": "1.0.0.0",
"parameters": {
"name": {
"value": "azinsider"
},
"location": {
"value": "eastus"
},
"environmentId": {
"value": "/subscriptions/d988cbee-043f-4c46-9a59-dedb2119e48c/resourceGroups/azinsider_demo/providers/Microsoft.App/managedEnvironments/managedEnvironment-azinsiderdemo"
},
"containers": {
"value": [
{
"name": "simple-hello-world-container",
"image": "mcr.microsoft.com/azuredocs/containerapps-helloworld:latest",
"command": [],
"resources": {
"cpu": 0.25,
"memory": ".5Gi"
}
}
]
},
"registries": {
"value": []
},
"secrets": {
"value": {
"arrayValue": []
}
},
"ingress": {
"value": {
"external": true,
"targetPort": 80
}
},
"environmentName": {
"value": "managedEnvironment-azinsiderdemo"
},
"workspaceName": {
"value": "workspaceazinsiderdemo"
},
"workspaceLocation": {
"value": "eastus"
}
}
}
5. Azure Bicep Template — Deployment
We will use the command below to deploy our Bicep template:
$date = Get-Date -Format "MM-dd-yyyy"
$rand = Get-Random -Maximum 1000
$deploymentName = "AzInsiderDeployment-"+"$date"+"-"+"$rand"
New-AzResourceGroupDeployment -Name $deploymentName -ResourceGroupName azinsider_demo -TemplateFile .\main.bicep -TemplateParameterFile .\azuredeploy.parameters.json -c
The image below shows the preview of the deployment:
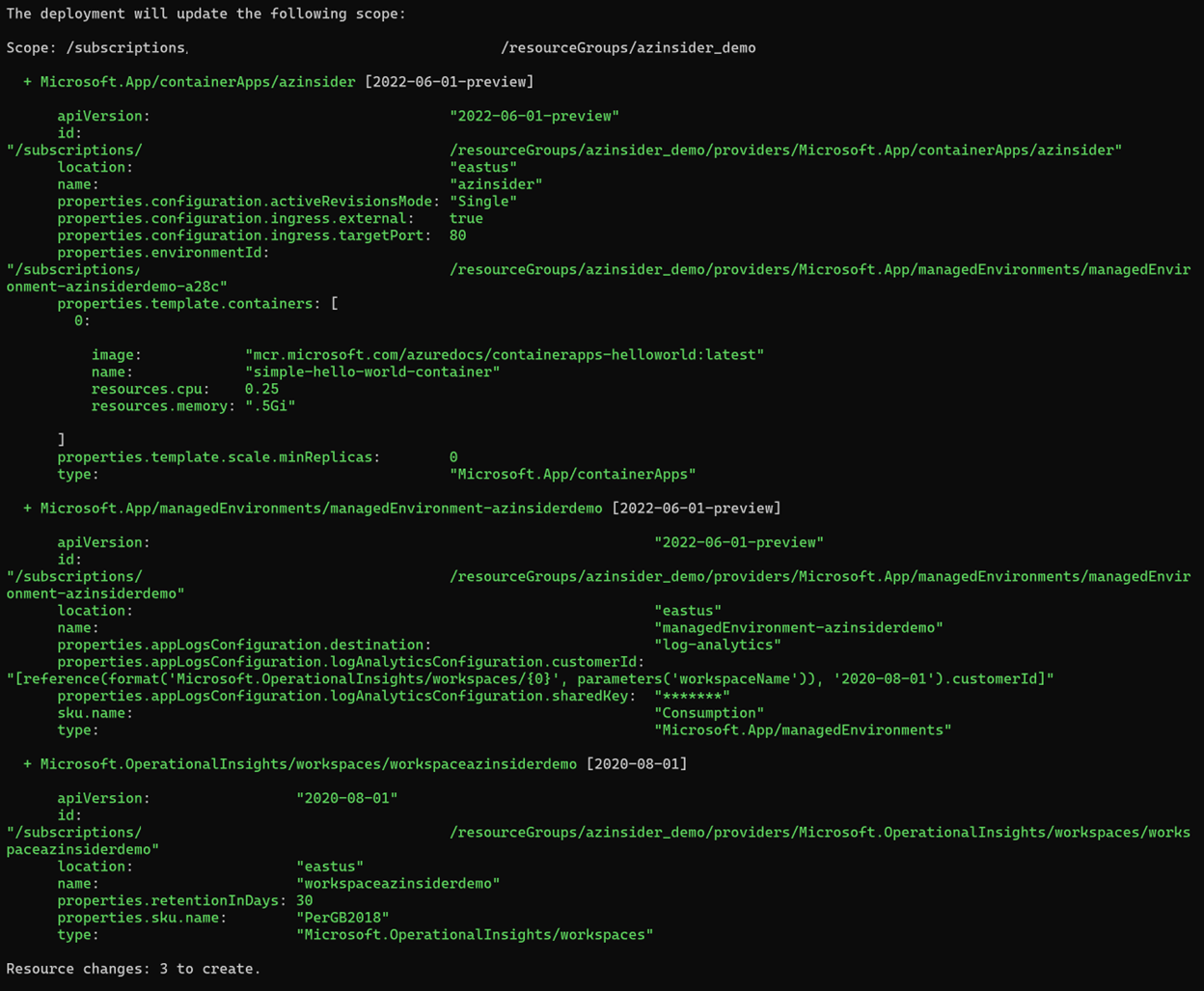
Then we will execute the deployment. The image below shows the deployment output:
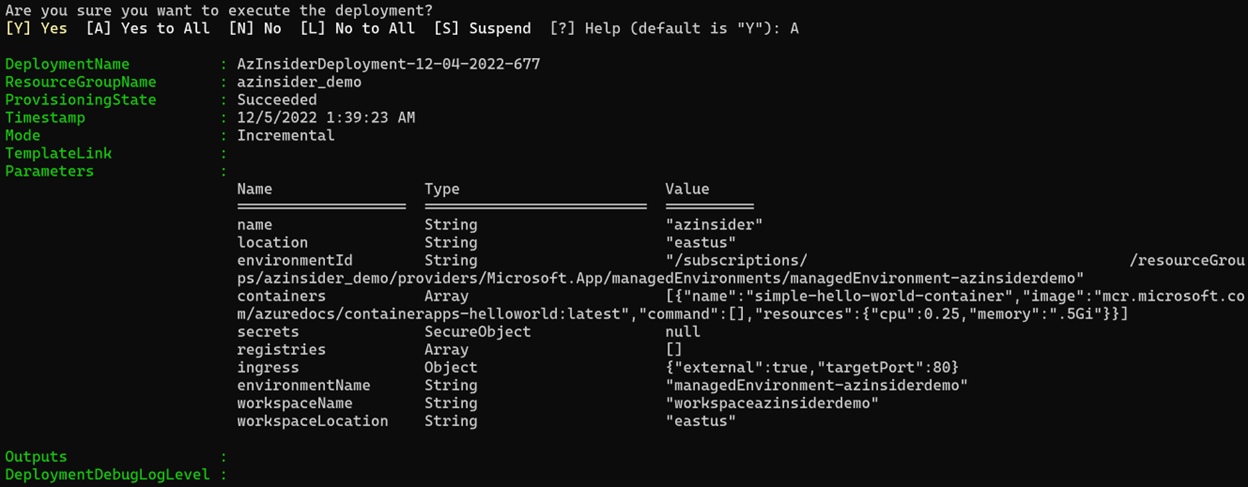
You can also check the deployment using the Azure Portal.
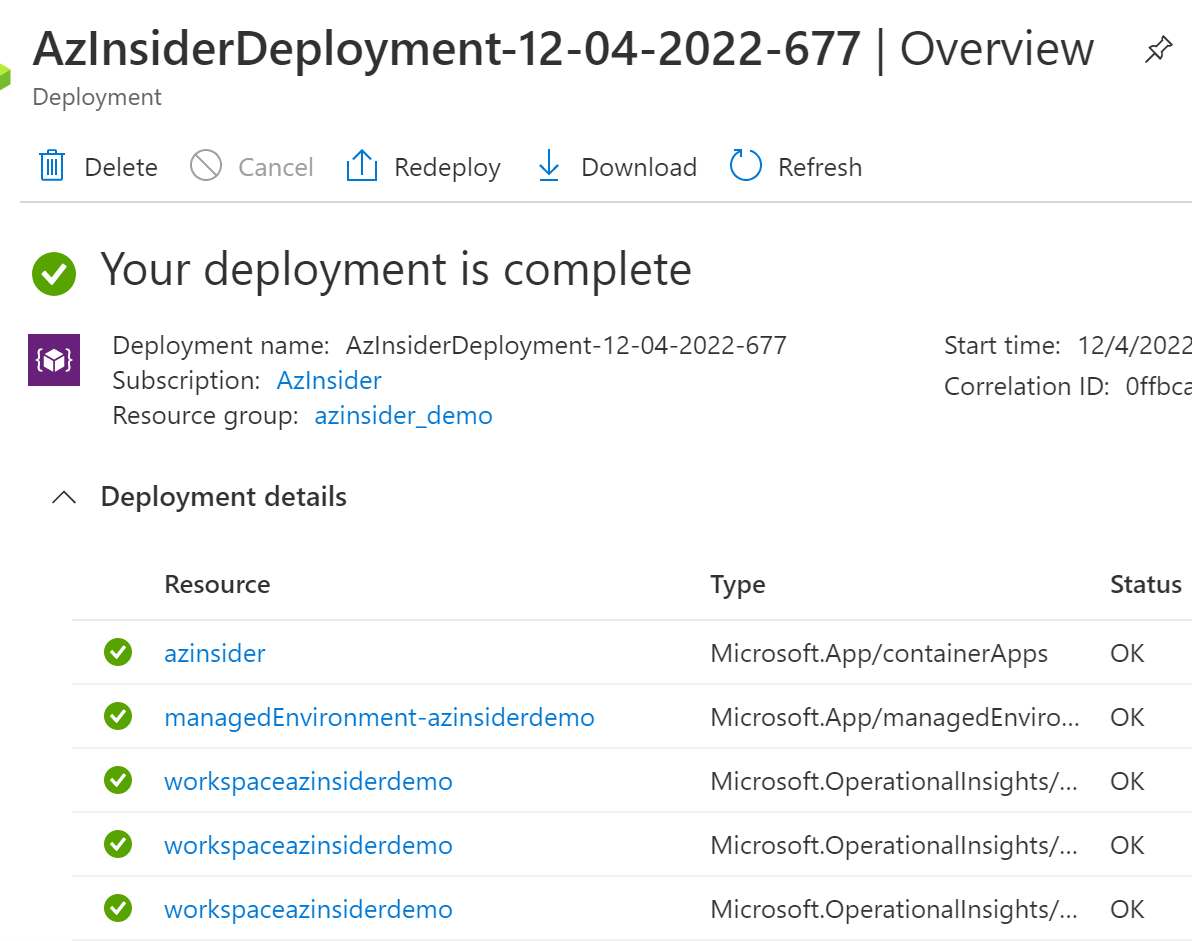
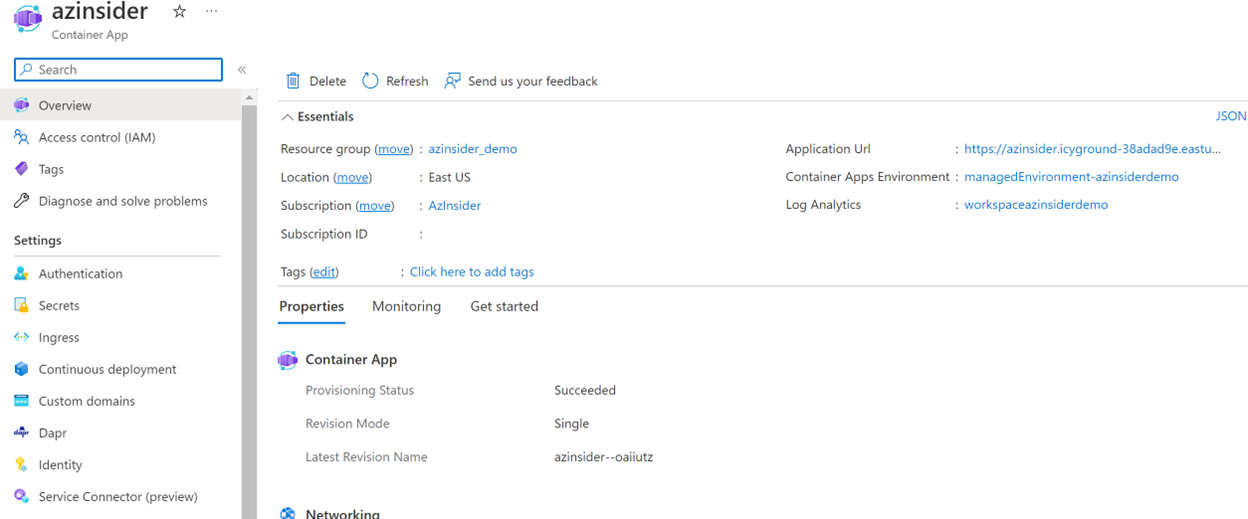
Source Code
You can find the code of this solution in the following URL, feel free to contribute!
https://github.com/daveRendon/azinsider/tree/main/application-workloads/azure-container-apps

